Install Matrix Home Server On Kubernetes¶
Preface¶
What is Matrix?
Quote
Matrix is an open standard for interoperable, decentralised, real-time communication over IP. It can be used to power Instant Messaging, VoIP/WebRTC signalling, Internet of Things communication - or anywhere you need a standard HTTP API for publishing and subscribing to data whilst tracking the conversation history.
Link: https://matrix.org/faq/#what-is-matrix%3F
So we are about to install a private real time messaging (Chat) server. It can be useful for you if you want to replace Whatsapp, Telegram, FB messenger, Viber, etc, or just want your own messaging server. Or if you don't trust in these services and want a service which focuses on your privacy. Another question is how your partners with whom you want to chat trust your server.
I'm wondering if you have ever thought about having your own messaging server. If the answer is yes, it's time to build one. I hope you will easily achieve this with the help of this article.
Requirements¶
- First and most important to have a valid domain name. If you don't have any you can pick up one free from DuckDNS
- Installed Kubernets cluster
- Public Internet access.
- At least 2 GB of free RAM.
I assume you build this server for your family and friends, and don't want to share with the whole World. For some tens of people you don't need to purchase an expensive server, but according to the number of attachments (file, pictures, videos,etc) you may need some hundreds of GB disk space.
Docker Compose¶
Maybe the easiest way to install everything all together is writing a Docker compose file. The compose file below can be used with docker-compose command or as Stack in Portainer. Later in this article we will use this compose file as reference for writing the Kubernetes manifest files (cm, deployment, sevice, pvc, etc).
| Click Here For Raw Source | |
|---|---|
| |
You can see that we have 3 services:
- matrix : The Matrix server
- caddy : Web server for use as reverse proxy.
- You can use any other web server you like (eg.: Apache httpd, Nginx)
- I chose Caddy because it is super easy to configure as a reverse proxy and supports automatic SSL certificate generation and maintenance.
- postgres : Database engine.
- You can skip this if you want to use the default sqlite engine, but it is not recommended for daily (production) use.
Before you up this compose file create the necessary directories:
Matrix process run as 991 userID and groupID so we need to run chown command:
Generate The Matrix Config File¶
For generating the initial config files please follow these steps:
| Command | |
|---|---|
Unable to find image 'matrixdotorg/synapse:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from matrixdotorg/synapse
7d63c13d9b9b: Pull complete
7c9d54bd144b: Pull complete
6c659176d5c8: Pull complete
31bfadeaf52b: Pull complete
b0be2954cd61: Pull complete
24d50aa74e2c: Pull complete
1816510873a0: Pull complete
227c613c4a00: Pull complete
097ac90fbed0: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:2c74baa38d3241aaf4a059a7e7c01786ba51ac5fe6fcf473ede3eb148f9358ba
Status: Downloaded newer image for matrixdotorg/synapse:latest
Creating log config /data/matrix.vincze.work.log.config
Generating config file /data/homeserver.yaml
Generating signing key file /data/matrix.vincze.work.signing.key
A config file has been generated in '/data/homeserver.yaml' for server name 'matrix.vincze.work'. Please review this file and customise it to your needs.
| Command | |
|---|---|
data/
data/matrix.vincze.work.signing.key
data/matrix.vincze.work.log.config
config/
config/homeserver.yaml
Important
You have to change SYNAPSE_SERVER_NAME to point to your own domain.
Inititalize The Database¶
- Start the a postgres instance
| Command | |
|---|---|
Important
Use the same environment values as in the compose file!
You may want to check the logs:
You should see the following lines:
PostgreSQL init process complete; ready for start up.
2021-10-22 13:20:19.900 CEST [1] LOG: starting PostgreSQL 14.0 on x86_64-pc-linux-musl, compiled by gcc (Alpine 10.3.1_git20210424) 10.3.1 20210424, 64-bit
2021-10-22 13:20:19.900 CEST [1] LOG: listening on IPv4 address "0.0.0.0", port 5432
2021-10-22 13:20:19.900 CEST [1] LOG: listening on IPv6 address "::", port 5432
2021-10-22 13:20:19.974 CEST [1] LOG: listening on Unix socket "/var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432"
2021-10-22 13:20:20.042 CEST [51] LOG: database system was shut down at 2021-10-22 13:20:19 CEST
2021-10-22 13:20:20.077 CEST [1] LOG: database system is ready to accept connections
- Get into the container and create the user and database
docker exec -it postgres-init /bin/bash
createuser --pwprompt synapse_user
Enter password for new role:
Enter it again:
createdb --encoding=UTF8 --locale=C --template=template0 --owner=synapse_user synapse
exit
Info
If you use another user than root (POSTGRES_USER=root) add -U [USERNAME] paramter at the and of the commands. createuser --pwprompt synapse_user -U [USERNAME]
Warning
Note your provided password, you will need it when configuring Matrix!
- Remove The Container
Info
If something went wrong you can simply stop and remove the container and delete the content of the database directory.
rm -rf /opt/docker/matrix/postgres/*
And you can start over the init process of the database.
Edit homeserver.yaml¶
--- homeserver.yaml-org 2021-10-22 13:43:26.753645597 +0200
+++ homeserver.yaml 2021-10-22 13:45:27.948188284 +0200
@@ -742,25 +742,25 @@
#
# Example Postgres configuration:
#
-#database:
-# name: psycopg2
-# txn_limit: 10000
-# args:
-# user: synapse_user
-# password: synapse
-# database: synapse
-# host: localhost
-# port: 5432
-# cp_min: 5
-# cp_max: 10
+database:
+ name: psycopg2
+ txn_limit: 10000
+ args:
+ user: synapse_user
+ password: 12345678
+ database: synapse
+ host: matrix-postgres
+ port: 5432
+ cp_min: 5
+ cp_max: 10
#
# For more information on using Synapse with Postgres,
# see https://matrix-org.github.io/synapse/latest/postgres.html.
#
-database:
- name: sqlite3
- args:
- database: /data/homeserver.db
+#database:
+# name: sqlite3
+# args:
+# database: /data/homeserver.db
## Logging ##
Caution
Don't forget to remove sqlite3 related lines as the example shows.
Inititalize The Caddyfile¶
cd /opt/docker/matrix/caddy
docker run -it --entrypoint=/bin/sh caddy:latest -c "cat /etc/caddy/Caddyfile" >Caddyfile
This will create a minimal Caddyfile example. Actually this command does nothing than copy the Caddyfile from the container to the directory where you are.
Edit this file
You Caddyfile should look like this:
Start Everything¶
We are ready to start the Matrix HomeServer. Save the docker-compose.yaml file if you haven't already do that, and run:
And wait for up condition:
| Command | |
|---|---|
Name Command State Ports
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
matrix-postgres docker-entrypoint.sh postgres Up 5432/tcp
matrix-web-caddy caddy run --config /etc/ca ... Up 2019/tcp, 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp,:::443->443/tcp, 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp,:::80->80/tcp
synapse-matrix /start.py Up (healthy) 0.0.0.0:8008->8008/tcp,:::8008->8008/tcp, 8009/tcp, 8448/tcp
Check your matrix server:
Browser Screenshot:

Federation¶
What does federated mean?
Quote
Federation allows separate deployments of a communication service to communicate with each other - for instance a mail server run by Google federates with a mail server run by Microsoft when you send email from @gmail.com to @hotmail.com.
interoperable clients may simply be running on the same deployment - whereas in federation the deployments themselves are exchanging data in a compatible manner.
Matrix provides open federation - meaning that anyone on the internet can join into the Matrix ecosystem by deploying their own server.
In order to the federation work you need to modify the Caddyfile and docker-compose.yaml.
docker-compose.yaml
--- docker-compose.yaml 2021-10-23 16:31:16.567890416 +0200
+++ docker-compose.yaml-orig 2021-10-23 17:04:08.640359385 +0200
@@ -31,6 +31,7 @@
ports:
- 80:80
- 443:443
+ - 8448:8448
networks:
- matrix
postgres:
Caddyfile
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@
# this machine's public IP, then replace ":80" below with your
# domain name.
-matrix.vincze.work {
+matrix.vincze.work:443 matrix.vincze.work:8448 {
# Set this path to your site's directory.
root * /usr/share/caddy
@@ -24,4 +24,3 @@
# Refer to the Caddy docs for more information:
# https://caddyserver.com/docs/caddyfile
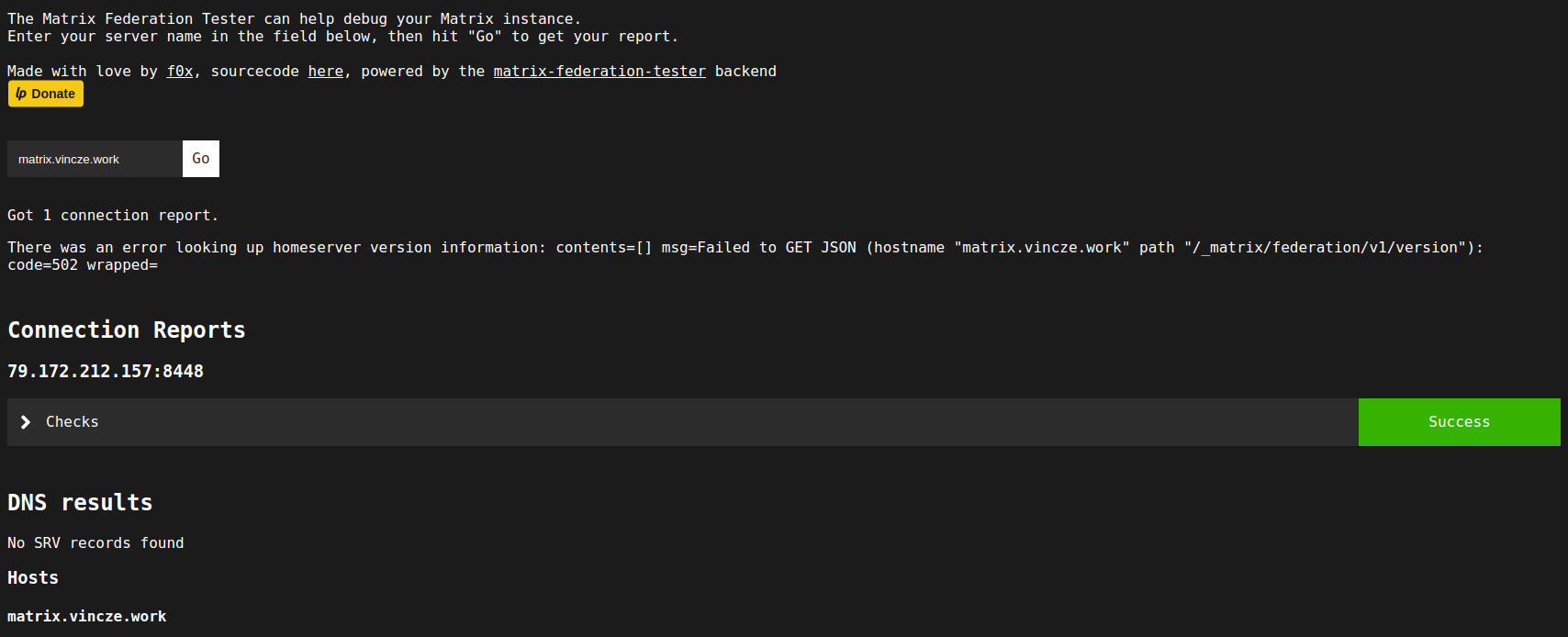
You can check if fedearation work or not: https://federationtester.matrix.org
ScreenShot:
Login¶
We don't have any user, yet. We have three option for registering new users:
- Enable registration in the homeserver.yaml (
enable_registration: true) - Use the
registration_shared_secret. - Or use command line interface inside the container.
I will show the third option:
- Get Into the container
- Register new user
register_new_matrix_user -u jvincze -p Matrix1234 -a -c /config/homeserver.yaml http://localhost:8008
- Open https://app.element.io/#/welcome in your browser
- Click on "Sign In"
- Change the "Homeserver" URL
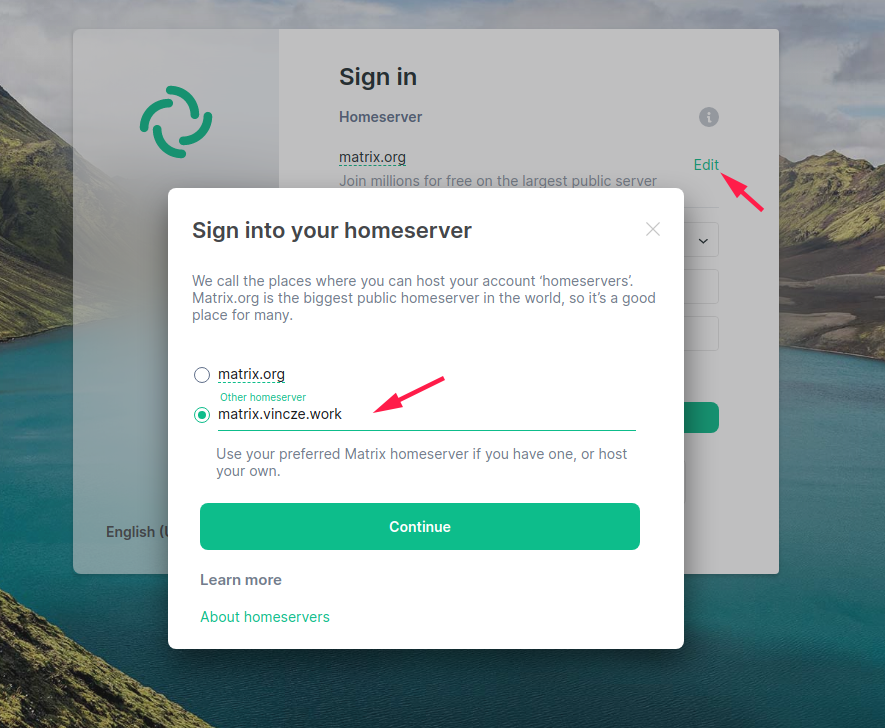
- Enter your credentials
And we are done. We have a fully functional Matrix Homeserver. Of course there are a lot of configurations available in the homesever.yaml, and I recommend going through this file at least once to get to know the possibilities.
We are going to deploy this minimal installation of Matrix to Kubernetes cluster in the next section.
Deploy To Kubernetes¶
Create the namespace¶
Prepare Matrix Configmap & Storage¶
- Generate the config files
mkdir -p /tmp/matrix/config /tmp/matrix/data
docker run -it --rm \
--mount type=bind,src=/tmp/matrix/config,dst=/config \
--mount type=bind,src=/tmp/matrix/data,dst=/data \
-e SYNAPSE_SERVER_NAME=matrix-kub-test.duckdns.org \
-e SYNAPSE_REPORT_STATS=yes \
-e SYNAPSE_CONFIG_DIR=/config \
-e SYNAPSE_CONFIG_PATH=/config/homeserver.yaml \
matrixdotorg/synapse:latest generate
- Create the Configmap & Secret
cd /tmp/matrix
kubectl -n matrix create cm matrix \
--from-file=homeserver.yaml=./config/homeserver.yaml \
--from-file=matrix-kub-test.duckdns.org.log.config=./config/matrix-kub-test.duckdns.org.log.config
kubectl -n matrix create secret generic matrix-key \
--from-file config/matrix-kub-test.duckdns.org.signing.key
- Create Persistent Volume
Download & Apply
curl -L -o /tmp/PersistentVolumeClaim-matrix.yaml \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jvincze84/jvincze84.github.io/master/docs/files/matrix/PersistentVolumeClaim-matrix.yaml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/matrix-pvc.yaml
Deploy Matrix Homeserver¶
First we deploy the Matrix homeserver without any configuration changes. Later we can update the homeserver.yaml in the Configmap.
| Click Here For Raw Source | |
|---|---|
| |
2023-04-28 - Permission denied
You may experince permission denied error on the mounted /data directory.
This is likely because your persistent volume provider mount the path with wrong uid/guid. Matirx uses 991:991 by default. So I added the followings to the Deployment manifest:
Download & Apply
curl -L -o /tmp/Deployment-matrix.yaml \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jvincze84/jvincze84.github.io/master/docs/files/matrix/Deployment-matrix.yaml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/Deployment-matrix.yaml
Check The Deployment
Create Service¶
Download & Apply
curl -L -o /tmp/Service-matrix.yaml \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jvincze84/jvincze84.github.io/master/docs/files/matrix/Service-matrix.yaml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/Service-matrix.yaml
Check The Service
Name: matrix
Namespace: matrix
Labels: k8s-app=postgres
Annotations: <none>
Selector: k8s-app=matrix
Type: ClusterIP
IP Family Policy: SingleStack
IP Families: IPv4
IP: 10.22.84.86
IPs: 10.22.84.86
Port: matrix 8008/TCP
TargetPort: 8008/TCP
Endpoints: 10.32.0.3:8008
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
Deploy Postgres SQL¶
Create The PersistentVolumeClaim¶
Download & Apply
curl -L -o /tmp/PersistentVolumeClaim-postgres.yaml \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jvincze84/jvincze84.github.io/master/docs/files/matrix/PersistentVolumeClaim-postgres.yaml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/PersistentVolumeClaim-postgres.yaml
Create Secret¶
This password will be used in the Deployment as the password of the initial user (POSTGRES_USER = matrix).
Deployment¶
| Click Here For Raw Source | |
|---|---|
| |
Download & Apply
curl -L -o /tmp/PersistentVolumeClaim-postgres.yaml \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jvincze84/jvincze84.github.io/master/docs/files/matrix/Deployment-postgres.yaml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/Deployment-postgres.yaml
Check The Pod & Logs
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
matrix-7658b9d5db-49kcc 1/1 Running 5 5d19h 10.32.0.3 kube-test.int.vinyosoft.info <none> <none>
postgres-7698969f95-8c4jn 1/1 Running 1 2d18h 10.32.0.8 kube-test.int.vinyosoft.info <none> <none>
2021-10-26 18:41:34.085 UTC [1] LOG: listening on Unix socket "/var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432"
2021-10-26 18:41:34.170 UTC [64] LOG: database system was shut down at 2021-10-26 18:41:33 UTC
2021-10-26 18:41:34.216 UTC [1] LOG: database system is ready to accept connections
Service¶
Download & Apply
curl -L -o /tmp/Service-postgres.yaml \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jvincze84/jvincze84.github.io/master/docs/files/matrix/Service-postgres.yaml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/Service-postgres.yaml
Check The Service
Name: postgres
Namespace: matrix
Labels: k8s-app=postgres
Annotations: <none>
Selector: k8s-app=postgres
Type: ClusterIP
IP Family Policy: SingleStack
IP Families: IPv4
IP: 10.22.24.132
IPs: 10.22.24.132
Port: postgres 5432/TCP
TargetPort: 5432/TCP
Endpoints: 10.32.0.8:5432
Session Affinity: None
Events: <none>
Check if the IP address and port of Endpoints are matching the Postgres POD IP address and port.
Connect Matix Homeserver To Postgres¶
Prepare The Databse¶
First we need to create a user and database for the homeserver, just like we did before in the compose section.
Modify The Homeserver Configmap¶
- Lines To Remove
- Lines To add:
database:
name: psycopg2
txn_limit: 10000
args:
user: synapse_user
password: 12345678
database: synapse
host: postgres.matrix.svc.cluster.local
port: 5432
cp_min: 5
cp_max: 10
Basically we are done with set up the Homeserver. There is only one thing to do, somehow publish the homeserver to the Internet.
Ingress¶
There are several options for accessing the Matrix Homeserver from the Internet. I don't know your architecture, but maybe you already have an Ingress Controller and a reverse proxy, etc...
I'll show some solutions:
- My setup at home looks something like this:
*.mydomain.hu --> Apache WebServer (reverse proxy) --> Kubernetes Ingress.- Wildcard certificate installed on the Apache WebSever.
- In this setup I need to create only an
Ingressin Kubernets and the Homserver immediately becomes accessible. - I recommend using a separate reverse proxy for the incoming connection to Kubernetes. This reverse proxy could be Apache, Nginx, Caddy, etc.
- If you don't have separate reverse proxy:
- You can set up Homeserver to listen on a https port:
matrix.mydomain.hu --> Ingress SSL Pass-through --> Homeserver (https). - Another way is to setup your
Ingressto listen on https:matrix.mydomain.hu --> Ingress (SSL) --> Homeserver (plain http)If you chose this option take a look at this page: https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/user-guide/tls/#automated-certificate-management-with-cert-manager - You can setup
Caddyon the Kubernetes:homeserver.mydomain.hu --> Ingress To Caddy (http) --> Caddy --> Homserver (service)
- You can set up Homeserver to listen on a https port:
I can't write example for the all available scenario, but I want to post here a working, overall solution, thus I show two examples:
Simple Ingress¶
If you have already a working architecture you may need only an Ingress like this:
Download & Apply
curl -L -o /tmp/Ingress-matrix.yaml \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jvincze84/jvincze84.github.io/master/docs/files/matrix/Ingress-matrix.yaml
kubectl apply -f /tmp/Ingress-matrix.yaml
Check Ingress
Name: matrix
Namespace: matrix
Address: 172.16.1.214
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 (<error: endpoints "default-http-backend" not found>)
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
matrix.k8s-test.loc
matrix:8008 (10.32.0.3:8008)
Annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 110m
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Sync 24s (x3 over 17m) nginx-ingress-controller Scheduled for sync
How Ingress - Service And Deployment Are Related?
If you want to know more about how these three things are related read the following article: https://dwdraju.medium.com/how-deployment-service-ingress-are-related-in-their-manifest-a2e553cf0ffb
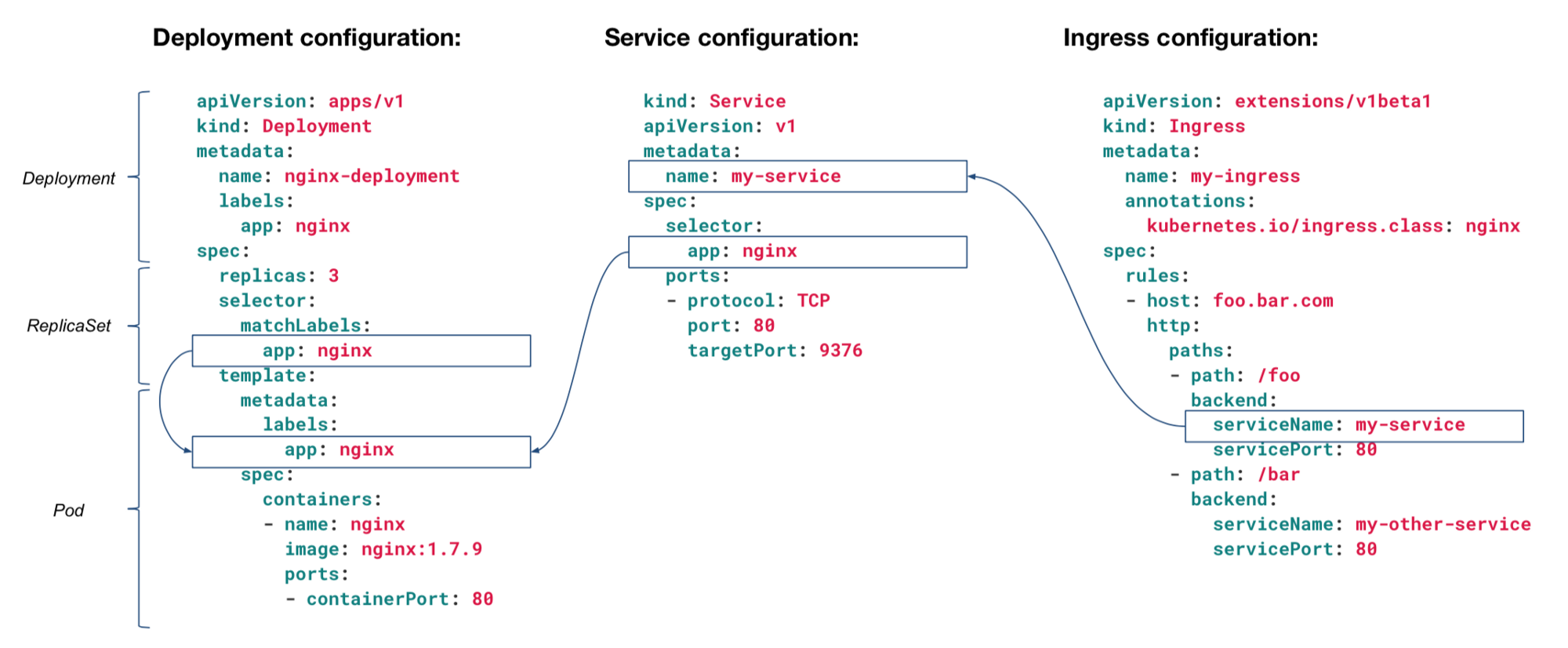
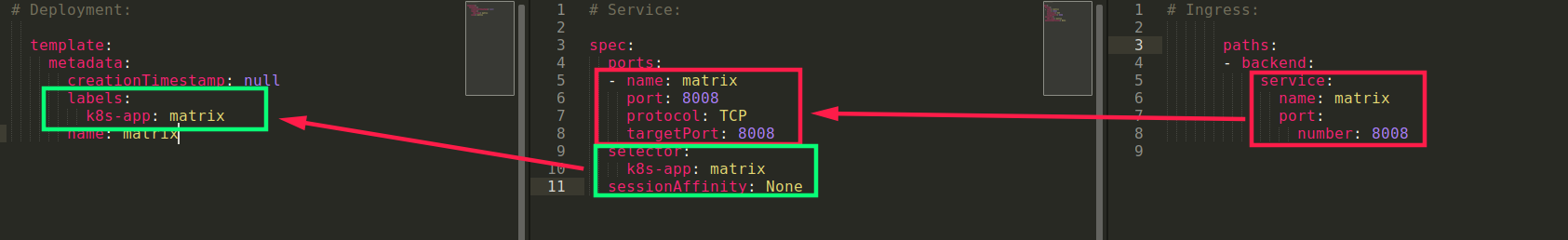
In our case, this the flow:
Cert Manager¶
First I wanted to write about Caddy here, but changed my mind. I think a much more suitable solution is using the Cert Manager.
My first thought was to deploy Caddy, setup as reverse proxy for the Matrix Service, and create an Ingress for Caddy. This would have been similar to what we did in the compose file before. I don't think anybody wants to use Ingress and Caddy in this way.
Documentations:
- https://cert-manager.io
- https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/user-guide/tls/#automated-certificate-management-with-cert-manager
I'm using Nginx Ingrees Controller for this demo. I won't write here a step-by-step installation about the Ingress controller. If you need detailed documentation please consult the official site: https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/deploy/, or see my single node Kubernetes installation article.
Install Cert Manager
Installing cert-manager is really simple, only one command:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/jetstack/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.6.0/cert-manager.yaml
For more details visit the official documentation here
ClusterIssuer
We are going to create two ClusterIssuer:
- Letsencrypt Staging
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging
spec:
acme:
email: jvincze84@gmail.com
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
- Letsencrypt Production
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-prod
spec:
acme:
email: jvincze84@gmail.com
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
preferredChain: "ISRG Root X1"
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-prod
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
Check:
NAME READY STATUS AGE
letsencrypt-prod True The ACME account was registered with the ACME server 49s
letsencrypt-staging True The ACME account was registered with the ACME server 5h31m
Create Ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 110m
name: matrix
namespace: matrix
spec:
rules:
- host: homeserver.matrix-kub-test.duckdns.org
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: matrix
port:
number: 8008
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
tls:
- hosts:
- homeserver.matrix-kub-test.duckdns.org
secretName: matrix-prod-ingress
That's all! :) If your Kubernetes Ingress accessible from the Internet on port 80 and 443 the certificate issued in some seconds.
Checks
If something is not working as expected, there are some resources you should check.
challenges acme.cert-manager.io/v1 true Challenge
orders acme.cert-manager.io/v1 true Order
certificaterequests cr,crs cert-manager.io/v1 true CertificateRequest
certificates cert,certs cert-manager.io/v1 true Certificate
clusterissuers cert-manager.io/v1 false ClusterIssuer
issuers cert-manager.io/v1 true Issuer
First check challenges:
NAME STATE DOMAIN AGE
matrix-prod-ingress-gptxf-1059591821-1281697531 pending homeserver.matrix-kub-test.duckdns.org 2m42s
You can see that the challenge is in pending state. You can check what could be the problem with the following command:
Example error message:
status:
presented: true
processing: true
reason: 'Waiting for HTTP-01 challenge propagation: failed to perform self check
GET request ''http://homeserver.matrix-kub-test.duckdns.org/.well-known/acme-challenge/lgUy6mCEhhbQ9n_v3w_C47cbVgc5Bfvoy6JW3oxrH1o'':
Get "http://homeserver.matrix-kub-test.duckdns.org/.well-known/acme-challenge/lgUy6mCEhhbQ9n_v3w_C47cbVgc5Bfvoy6JW3oxrH1o":
dial tcp 87.97.31.112:80: i/o timeout (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting
headers)'
state: pending
Info
Just for reference, in my case the problem was that hairpin NAT wasn't set up properly in my router.
Check certificaterequests and certificates
NAME APPROVED DENIED READY ISSUER REQUESTOR AGE
certificaterequest.cert-manager.io/matrix-prod-ingress-gptxf True True letsencrypt-prod system:serviceaccount:cert-manager:cert-manager 19m
NAME READY SECRET AGE
certificate.cert-manager.io/matrix-prod-ingress True matrix-prod-ingress 19m
Your certificate is stored in this Secret: secretName: matrix-prod-ingress
Final Thoughts¶
I hope this article contains a lot of useful examples, use cases and help you to build your own Matrix Homeserver.
Of course there are any other options to deploy the Homeserver to Kubernetes, the way I showed here contains many useful examples on how to use docker-compose, service, ingress, cert-manager, configmap, secret, etc...